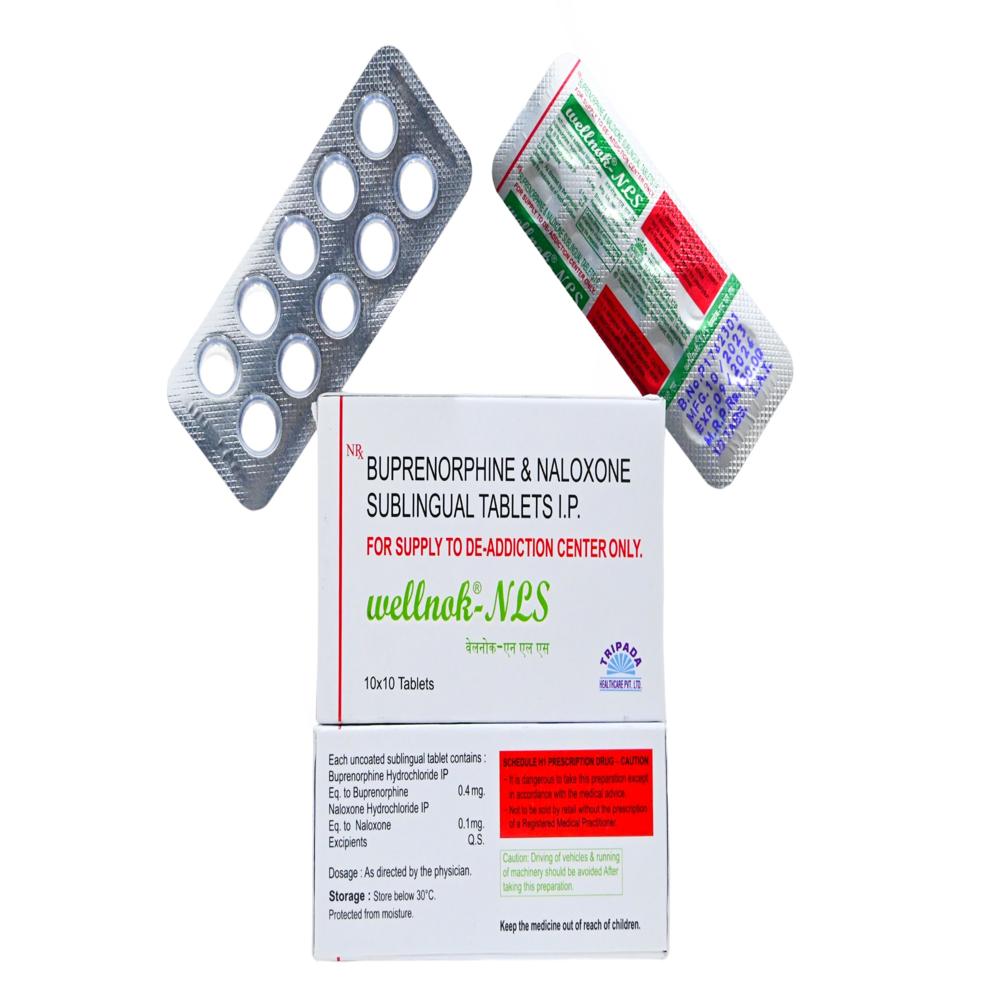
BUPRNORPHIN AND NALOXONE TABLETS
BUPRNORPHIN AND NALOXONE TABLETS Specification
- Form
- Tablet
- Purity
- High
- Shelf Life
- 1 Years
- Storage Instructions
- Cool & dry place
BUPRNORPHIN AND NALOXONE TABLETS Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 10 Strips
- Supply Ability
- 1000 Strips Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 7 Days
About BUPRNORPHIN AND NALOXONE TABLETS
Exerts its analgesic effect by binding to the muopioid receptors in the CNS It has a longer duration of analgesic action than morphine Its partial agonist activity gives it a low level of physical dependence Buprenorphine and morphine show similar doserelated resp depressant effectMixed opiate agonistantagonist buprenorphine combined with naloxone an opiate antagonist naloxone is included as an abuse deterrent Used for induction treatment in patients dependent on heroin or other shortacting opioids who are in opioid withdrawal also used for maintenance treatment of opioid dependence and narcotic painkillersAlso approved for use in adults to treat opioid dependence which is now called OUD With OUD opioids are chronically misused which means theyre taken in a way other than how theyre prescribed to be used With chronic misuse misuse happens over and over With dependence your body needs a drug in order for you to feel normal Buprenorphine tablets are part of a complete treatment program for OUD that usually includes counseling or psychotherapyNaloxone has an extremely high affinity for opioid receptors in the central nervous system A opioid receptor competitive antagonist and its rapid blockade of those receptors often produces rapid onset of withdrawal symptoms Also has an antagonist action though with a lower affinity at and opioid receptors Pharmacokinetics Naloxone is a pure opioid antagonist that acts competitively at opioid receptorsIndicationsAbuse deterrentOpioid dependenceaddiction narcotic painkillersOpioid withdrawalFAQs of BUPRNORPHIN AND NALOXONE TABLETS:
Q: What is the purity level of Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets?
A: Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets have a high purity level.Q: What is the form of Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets?
A: The product is available in tablet form.Q: What is the shelf life of Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets?
A: The shelf life of the product is 1 year.Q: What are the recommended storage conditions for Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets?
A: The tablets should be stored in a cool and dry place.Q: Are there specific storage instructions to maintain the quality of Buprenorphin and Naloxone Tablets?
A: Yes, to ensure quality, the tablets should be kept in a cool and dry environment.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
More Products in Antidepressant And Anti Anxiety Medicine Category
NORTRIPTYLINE-10 MG.
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Strips
Form : Tablet
Shelf Life : 24 TO 36 Months
Grade : Pharmaceutical Grade
Color : Other
TRIFLUOPERAZINE-5 MG. & TRIHEXYPHENIDYL-2 MG. TABLETS
Price 30.0 INR / Unit
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Units
Form : Tablet
Shelf Life : 1224 Months
Color : White
BUPRNORPHINE 2 MG TABLETS
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Strips
Form : Tablet
Shelf Life : 24 TO 36 Months
Grade : Pharmaceutical Grade
Color : White
VENLAFAXINE HCL-150 MG. EXTENDED RELEASE
Price 1100 INR / Box
Minimum Order Quantity : 10 Boxes
Form : Tablet
Shelf Life : 36 Months
Grade : Pharmaceutical Grade
Color : White
We deals only in bulk orders.